
Nephrons Structure Cortical and Juxtamedullary Nephrons, and Renal
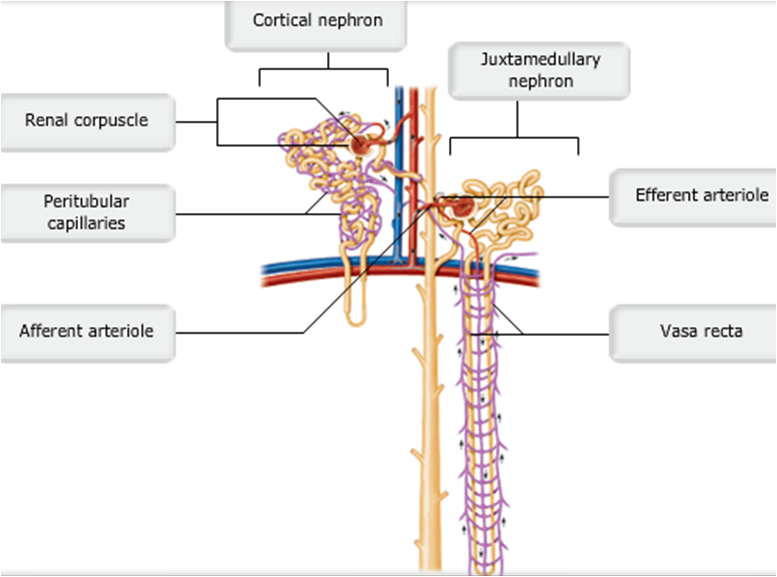
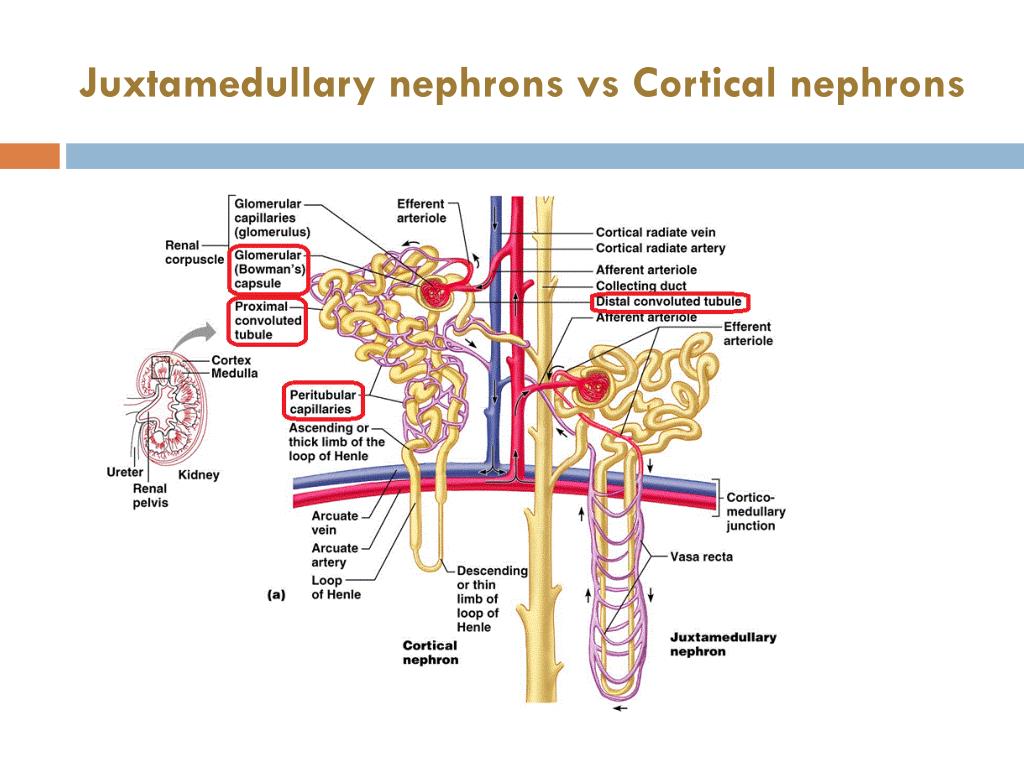
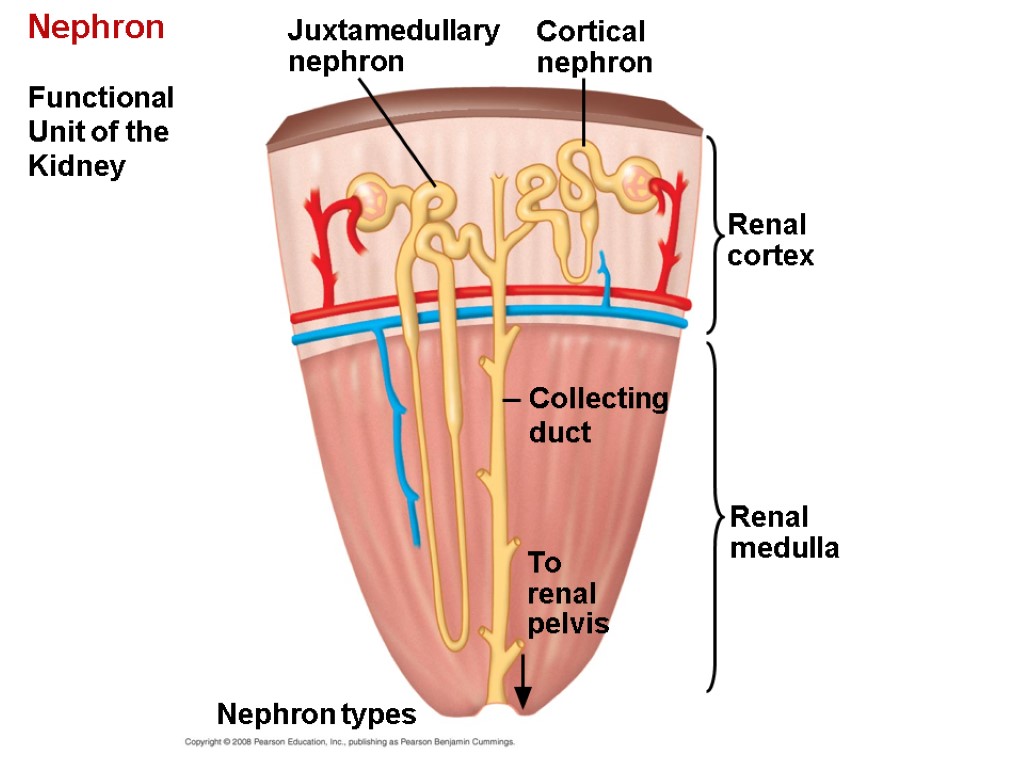
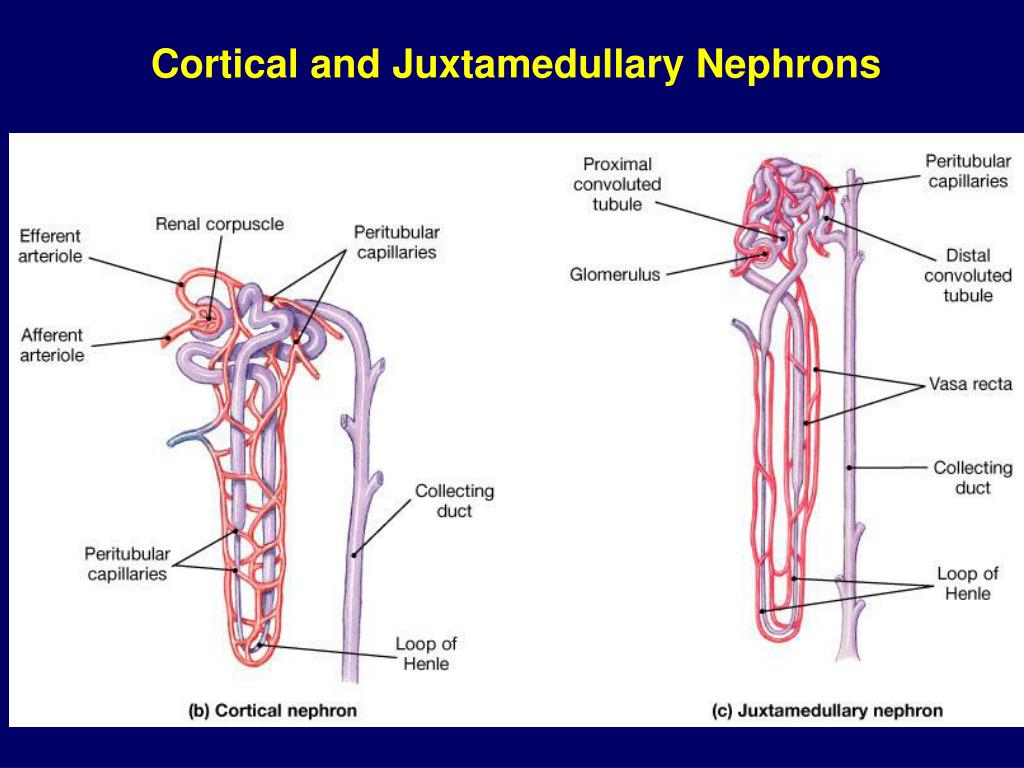
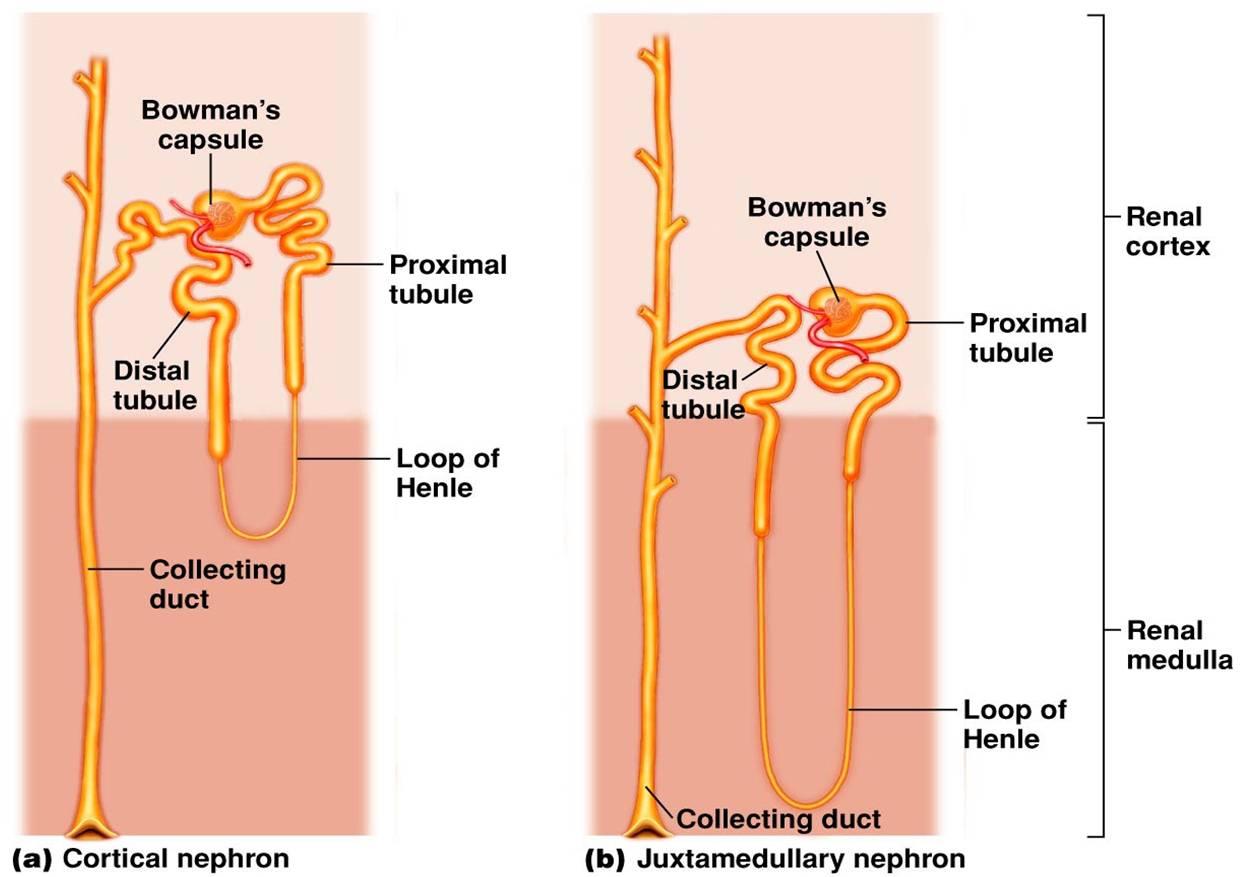
Anatomical Relations. Each nephron consists of a renal corpuscle and the associated renal tubule. In cortical nephrons, the renal corpuscle is located in the outer cortex of the kidney; their renal tubules are short and extend through the cortex and dip into the outer medulla. The nephron is surrounded by a complex network of capillaries which.
Print A&P II Test 4 flashcards Easy Notecards
Nephrons have two lengths with different urine-concentrating capacities: long juxtamedullary nephrons and short cortical nephrons. The four mechanisms used to create and process the filtrate (the result of which is to convert blood to urine) are filtration, reabsorption, secretion and excretion.

Difference b/w Cortical & Juxtamedullary Nephrons Loop of henle
Juxtamedullary nephron is a microscopic structural and functional unit of the kidney with a long loop of Henle extending deep into the renal medulla. The renal corpuscles of these nephrons are situated close to the renal medulla. Juxtamedullary nephrons occur only in birds and mammals.
PPT Tubular reabsorption & Secretion PowerPoint Presentation ID6567788
Renal pathologies can be grossly categorized depending on the affected segment of the nephron: the glomerulus, tubules, interstitium, or blood supply. Each one differs in clinical manifestations, making it vital for the clinician to integrate differential diagnoses.

Kidney Microanatomy (Lesson) Human Bio Media
The left kidney is located at about the T12 to L3 vertebrae, whereas the right is lower due to slight displacement by the liver. Upper portions of the kidneys are somewhat protected by the eleventh and twelfth ribs ( Figure 25.7 ). Each kidney weighs about 125-175 g in males and 115-155 g in females. They are about 11-14 cm in length, 6.
Chapter 44 Osmoregulation and Excretion. Overview A Balancing
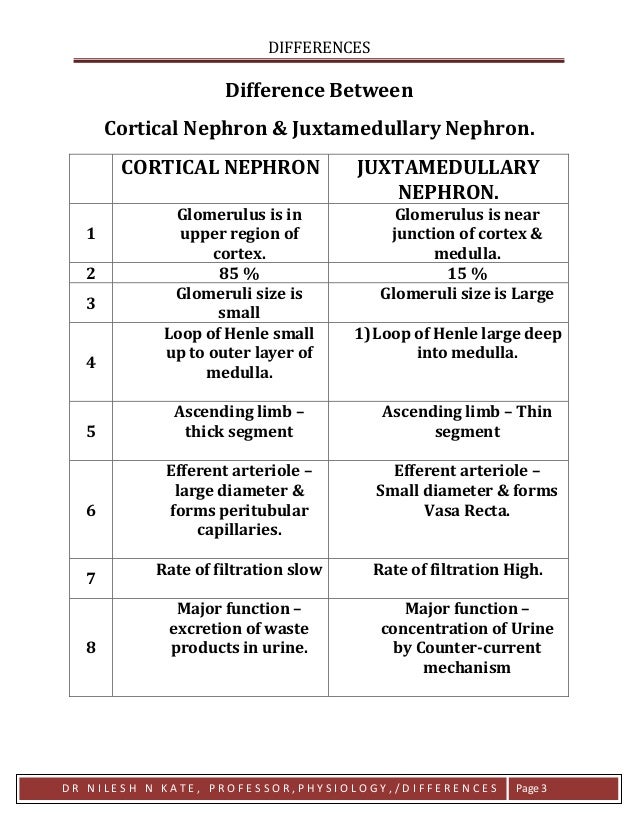
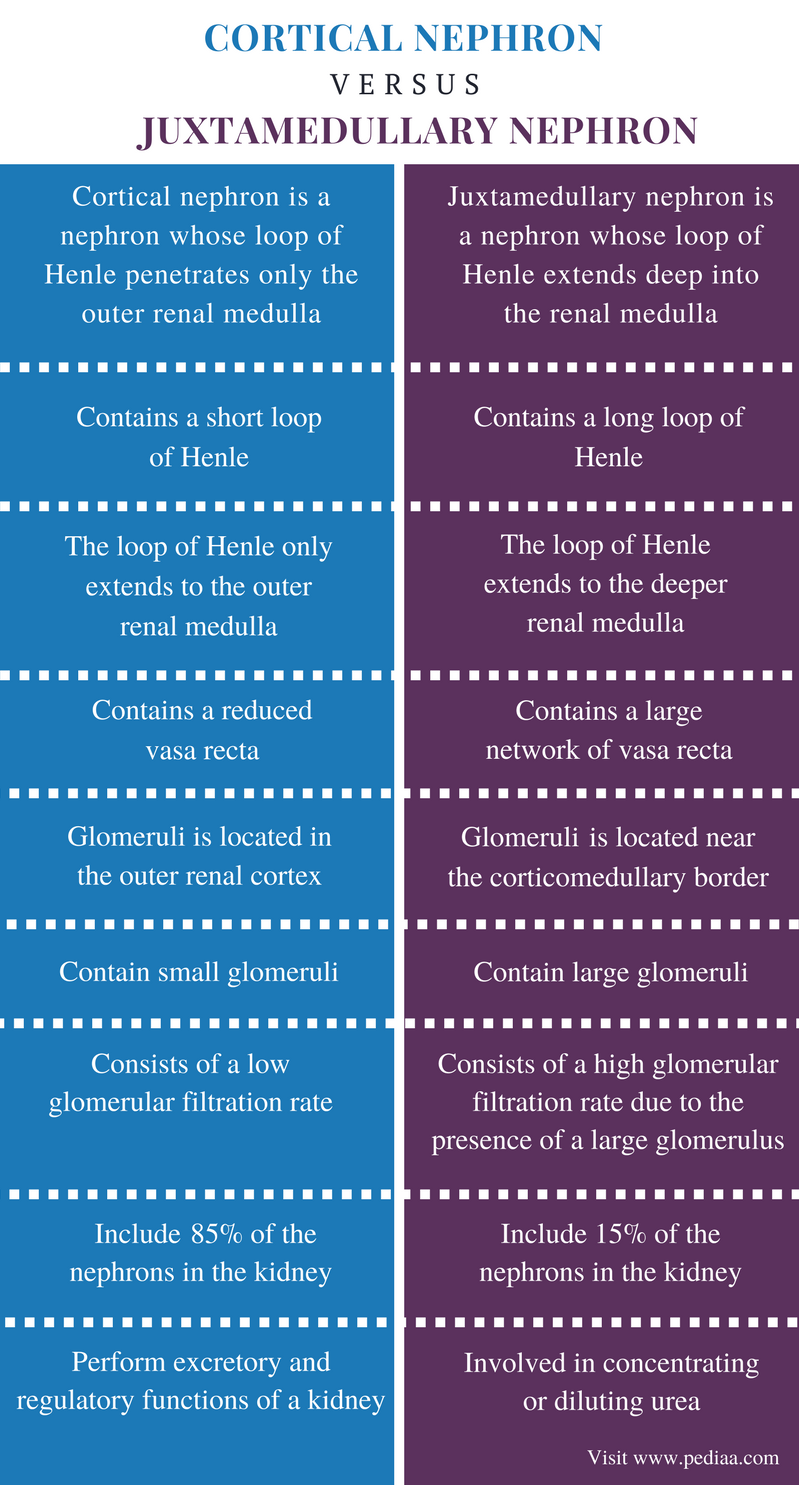
Differences: Cortical Nephron and Juxtamedullary Nephron The following table highlights the major differences between Cortical Nephron and Juxtamedullary Nephron − Conclusion In summary, while both cortical and juxtamedullary nephrons perform similar functions, there are some differences in their structure and function.

Fisiología Renal Parte I WFSA Resources
The kidneys contain two types of nephrons, superficial cortical nephrons (70-80%) and juxtamedullary nephrons (20-30%). These names refer to the location of the glomerular capsule, which is either in the outer cortex of the kidney, or near the corticomedullary border.

Cortical and Juxtamedullary nephrons and their associated blood vessels
There are Two main types of nephrons #Juxtamedullary and #Cortical nehrons. The detailed difference between the cortical and juxtamedullary nephron are cover.

The Urinary System Kidneys in 2022 Basic anatomy and physiology
For example, the cortical nephron is located in the cortex of the kidney, while the juxtamedullary nephron is located in the medulla of the kidney. Both are important for filtering blood, but some people have no idea what makes cortical and juxtamedullary nephron so different.
PPT Renal Physiology PowerPoint Presentation ID332876
This means that juxtamedullary nephrons are closer to the renal pelvis, which is the area where urine is collected. Filtration. Cortical nephrons filter blood at a slower rate than juxtamedullary nephrons. This is because cortical nephrons have a shorter loop of Henle, which is the part of the nephron that filters the blood.

Physiological base of Human Movement Lecture 9 UTS sport and society
Those nephrons that don't go deep into the medulla are called cortical nephrons (because their glomeruli are in the cortex), and those that go deeper are juxtamedullary nephrons (because their.

cortical nephron Google Search Loop of henle, Anatomy and
VDOMDHTMLtml> Cortical and Juxtamedullary Nephrons: Anatomy and Physiology - YouTube Dr. O is building an entire video library that will allow anyone to learn Microbiology and Anatomy &.

Structure Of Kidney Nephron Structure And Function Youtube Otosection
Cortex renis 1/4 Synonyms: Cortex renalis The kidneys are paired retroperitoneal organs of the urinary system. Their function is to filter blood and produce urine. Each kidney consists of a cortex, medulla and calyces. The nephron is the main functional unit of the kidney, in charge of removing metabolic waste and excess water from the blood.
Nephron Introduction, Structure and Function
Cortical Vs. Juxtamedullary Nephrons.. The glomerulus, a tiny network of capillaries, is found at the start of each cortical nephron in the outer renal cortex. The glomerulus filters blood that enters the renal artery circulation through the afferent arteriole. Water, ions, amino acids, glucose, and other tiny molecules are filtered during.
Differences cortical vs juxtamedullary nephron
The main difference between cortical nephron and juxtamedullary nephron is that cortical nephron contains a short loop of Henle which only extends into the outer region of the renal medulla whereas juxtamedullary nephron contains a longer loop of Henle which extends deeper into the inner medulla.
Difference Between Cortical Nephron and Juxtamedullary Nephron
Have you ever wondered about the fascinating differences that exist within this vital organ? In this article, we delve into the world of nephrons, the microscopic units within the kidneys, and specifically explore the disparities between cortical and juxtamedullary nephrons.